Precision Medicine in Gastroenterology
The field of gastroenterology has seen transformative advancements thanks to precision medicine, leading to significant improvements in diagnosing and treating gastrointestinal disorders. A recent breakthrough in using genetic profiling to tailor treatment for Crohn's disease patients exemplifies the profound impact of precision medicine. This blog will explore the role of precision medicine in diagnosing and treating gastrointestinal disorders, highlighting its potential to revolutionize patient care.
Understanding Gastrointestinal Disorders
Gastrointestinal (GI) disorders encompass a wide range of conditions affecting the digestive tract, including the esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, and gallbladder. These disorders can significantly impact an individual's quality of life and, in severe cases, can be life-threatening. The prevalence of GI disorders has increased over the years, making it a critical area of focus in healthcare.
Examples
Common gastrointestinal disorders include:
- Crohn’s Disease: A chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that can affect any part of the GI tract, causing symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and weight loss.
- Ulcerative Colitis: Another form of IBD, primarily affecting the colon and rectum, leading to inflammation and ulcers in the digestive tract lining.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): A functional GI disorder characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, and altered bowel habits without any visible signs of disease in the digestive tract.
- Celiac Disease: An autoimmune disorder where ingestion of gluten leads to damage in the small intestine.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): A chronic condition where stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation.
The Role of Precision Medicine
Precision medicine in gastroenterology involves tailoring medical treatment to the individual characteristics of each patient. This approach leverages genetic, biomarker, and molecular data to develop personalized treatment plans.
Genetic Profiling
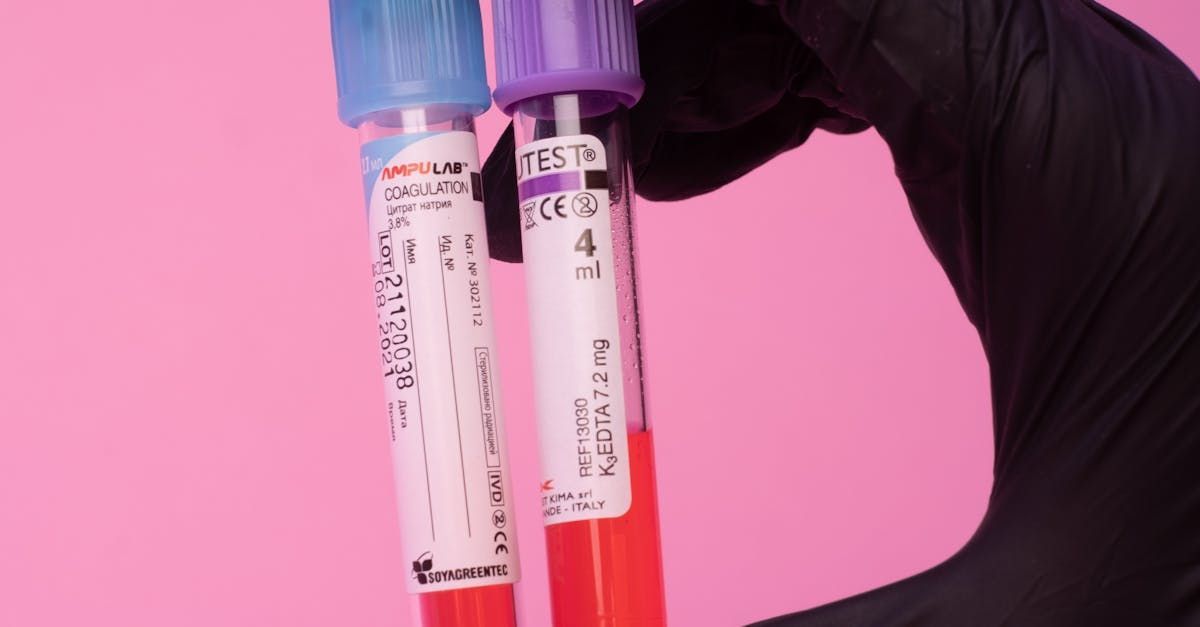
Genetic profiling plays a crucial role in understanding and treating GI disorders. By analyzing a patient’s genetic makeup, healthcare providers can identify mutations and genetic predispositions that contribute to the development and progression of these conditions. For instance, genetic variations in the NOD2 gene are associated with an increased risk of developing Crohn’s disease. Understanding these genetic factors helps in predicting disease risk and tailoring preventive measures and treatments.
Biomarkers
Biomarkers are biological molecules found in blood, other body fluids, or tissues that signal a normal or abnormal process, or a condition or disease. In gastroenterology, biomarkers are used for diagnosis, disease monitoring, and treatment response. For example, fecal calprotectin is a biomarker used to assess inflammation in IBD patients. High levels of calprotectin indicate active inflammation, helping clinicians adjust treatment plans accordingly.
Personalized Treatments
Personalized treatment plans are developed based on genetic and molecular data, ensuring that patients receive the most effective therapies with minimal side effects. For example, patients with Crohn’s disease may respond differently to various biologic therapies. Precision medicine enables the selection of the most suitable biologic based on the patient’s genetic profile, leading to better outcomes and reduced trial-and-error in treatment.
Technological Innovations
Genomic Sequencing
Genomic sequencing has revolutionized the field of precision medicine by allowing detailed analysis of an individual’s DNA. In gastroenterology, genomic sequencing helps identify genetic mutations associated with GI disorders. For instance, sequencing the genome of patients with IBD can reveal mutations that influence disease susceptibility and treatment response, guiding the development of targeted therapies.
AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are transforming precision medicine by analyzing large datasets to identify patterns and predict disease progression and treatment outcomes. In gastroenterology, AI algorithms can process genetic, clinical, and lifestyle data to predict which patients are at risk of developing certain GI disorders or who will respond best to specific treatments. This predictive capability enhances early intervention and personalized care.
Digital Health Tools
Digital health tools, such as mobile apps and wearable devices, are increasingly being used to manage GI disorders. These tools allow patients to track their symptoms, medication adherence, and lifestyle factors, providing valuable data for healthcare providers. For example, a mobile app designed for IBD patients can monitor symptoms and medication use, enabling timely adjustments to treatment plans and improving disease management.
How Notable Labs is Pioneering Precision Medicine in Gastroenterology
Notable Labs is at the forefront of integrating precision medicine into gastroenterology, leveraging advanced genetic and molecular analyses to develop personalized treatment plans for gastrointestinal disorders. By utilizing innovative technologies and collaborating with leading research institutions, Notable Labs is pioneering new approaches to diagnose, monitor, and treat conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Their commitment to precision medicine exemplifies the potential to transform patient care, improve outcomes, and pave the way for a future of personalized healthcare in gastroenterology.
Innovative Genetic and Molecular Analyses
Notable Labs employs cutting-edge genetic and molecular analysis techniques to gain a deeper understanding of gastrointestinal disorders at the individual level. By sequencing patients' genomes and analyzing their molecular profiles, Notable Labs can identify specific genetic mutations and biomarkers associated with conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. This detailed genetic information allows for the development of highly personalized treatment plans that target the unique underlying causes of each patient’s condition.
Advanced Diagnostic Technologies
Notable Labs utilizes state-of-the-art diagnostic technologies to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of diagnosing gastrointestinal disorders. Technologies such as next-generation sequencing (NGS) and advanced imaging techniques enable the precise identification of genetic and molecular abnormalities. This level of precision in diagnostics ensures that patients receive the most appropriate and effective treatments from the outset, minimizing the trial-and-error approach often associated with conventional treatment methods.
Collaborative Research Initiatives
Notable Labs collaborates with leading research institutions and healthcare providers to drive innovation in precision medicine for gastroenterology. These partnerships facilitate the sharing of data, resources, and expertise, accelerating the development of new diagnostic tools and treatment options. By working closely with academic researchers and clinical practitioners, Notable Labs ensures that its precision medicine approaches are informed by the latest scientific discoveries and clinical best practices.
Personalized Treatment Plans
The cornerstone of Notable Labs’ approach is the development of personalized treatment plans based on each patient’s genetic and molecular data. For example, patients with Crohn’s disease may receive biologic therapies specifically chosen to target their unique genetic mutations. This personalized approach not only improves the effectiveness of treatments but also reduces the likelihood of adverse side effects, leading to better patient outcomes and higher quality of life.
Real-Time Disease Monitoring
Notable Labs leverages digital health tools and biomarkers to enable real-time monitoring of disease progression and treatment response. Patients can use mobile apps and wearable devices to track their symptoms, medication adherence, and lifestyle factors, providing continuous data to their healthcare providers. This real-time monitoring allows for timely adjustments to treatment plans, ensuring that patients receive the most effective care throughout their treatment journey.
Transforming Patient Care
By integrating precision medicine into gastroenterology, Notable Labs is transforming patient care. Their innovative approaches lead to earlier and more accurate diagnoses, more effective and personalized treatments, and improved long-term outcomes for patients with gastrointestinal disorders. This patient-centered approach exemplifies the potential of precision medicine to revolutionize healthcare, providing hope and improved quality of life for those affected by chronic and complex conditions.
Future Directions and Opportunities
Notable Labs continues to push the boundaries of precision medicine in gastroenterology, exploring new technologies and treatment paradigms. Emerging therapies, such as gene editing and advanced biologics, hold promise for further enhancing the precision and effectiveness of treatments. Collaborative research and policy support will be crucial in advancing these innovations and ensuring that all patients can benefit from the latest advancements in precision medicine.
In summary, Notable Labs is leading the charge in integrating precision medicine into gastroenterology. Their commitment to leveraging genetic and molecular analyses, advanced diagnostic technologies, and personalized treatment plans is setting a new standard for patient care. Through collaboration and innovation, Notable Labs is paving the way for a future where precision medicine transforms the diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal disorders, offering patients hope for better health and improved outcomes.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Case Study 1: Successful Use of Precision Medicine in Treating Crohn’s Disease
A patient with Crohn’s disease experienced multiple flares despite conventional treatment. Genomic sequencing revealed a specific genetic mutation associated with a poor response to standard therapies. Based on this genetic information, the healthcare team prescribed a targeted biologic therapy tailored to the patient’s genetic profile. The patient responded well to the new treatment, achieving remission and significantly improving their quality of life. This case highlights the potential of precision medicine to tailor treatments based on individual genetic profiles, leading to better outcomes.
Case Study 2: Personalized Treatment Approaches for Ulcerative Colitis
A patient with ulcerative colitis struggled with frequent flare-ups and severe symptoms. Through biomarker analysis, high levels of a specific inflammatory marker were detected, indicating active disease. The healthcare team used this information to adjust the patient’s treatment plan, introducing a new biologic therapy targeting the identified marker. The patient’s symptoms improved, and they achieved sustained remission. This success story demonstrates the importance of biomarkers in guiding personalized treatment decisions and improving patient outcomes.
Lessons Learned
These case studies underscore the importance of genetic profiling and biomarker analysis in developing personalized treatment plans. They illustrate how precision medicine can lead to better disease management, reduced side effects, and improved patient quality of life. Additionally, they highlight the need for continued research and collaboration to expand the application of precision medicine in gastroenterology.
Benefits of Precision Medicine for Gastrointestinal Disorders
Improved Outcomes
Precision medicine leads to better health outcomes by providing treatments tailored to the individual characteristics of each patient. By considering genetic, molecular, and clinical data, healthcare providers can select the most effective therapies, reducing the risk of adverse effects and improving disease management.
For example, personalized treatment plans for IBD patients based on genetic profiling and biomarker analysis have been shown to improve remission rates and reduce hospitalizations. This individualized approach ensures that patients receive the right treatment at the right time, leading to better overall outcomes.
Reduced Side Effects
One of the significant benefits of precision medicine is the ability to minimize side effects by targeting treatments specifically to the patient’s condition. Traditional treatments often involve a trial-and-error approach, which can result in unnecessary side effects and delayed improvement. Precision medicine reduces this risk by using genetic and molecular data to select the most appropriate therapies.
For instance, patients with a specific genetic mutation may be more susceptible to adverse effects from certain medications. Precision medicine enables the identification of these genetic factors, allowing healthcare providers to choose alternative treatments that are better tolerated by the patient.
Early Diagnosis and Intervention
Precision medicine facilitates early diagnosis and intervention, which are crucial for managing GI disorders effectively. Genetic profiling and biomarker analysis can identify individuals at risk of developing certain conditions before symptoms appear. Early detection allows for timely intervention, preventing disease progression and improving long-term outcomes.
For example, individuals with a family history of IBD can undergo genetic testing to assess their risk. If a high-risk genetic profile is identified, preventive measures and early treatment can be implemented, reducing the likelihood of severe disease development.
Challenges and Barriers
Technical Challenges
Despite its potential, precision medicine faces several technical challenges in the context of GI disorders. Analyzing genetic and molecular data requires advanced technologies and significant computational power. Additionally, integrating this data into clinical practice necessitates sophisticated infrastructure and expertise.
For example, genomic sequencing generates vast amounts of data that must be accurately interpreted to provide actionable insights. Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of these analyses is challenging, particularly when dealing with complex and variable genetic information. Addressing these technical challenges is essential for advancing precision medicine in gastroenterology.
Ethical Considerations
The use of genetic testing and biomarker analysis raises ethical considerations related to data privacy and informed consent. Genetic data is highly sensitive, and ensuring its confidentiality is paramount. Additionally, patients must fully understand the implications of genetic testing and provide informed consent before undergoing such procedures.
For instance, genetic testing can reveal information about an individual’s risk of developing other diseases or conditions, which may have implications for their family members. Healthcare providers must navigate these ethical considerations carefully, ensuring that patients are fully informed and that their privacy is protected.
Accessibility
Ensuring equitable access to precision medicine treatments is a significant challenge. Advanced genetic testing and personalized treatments can be costly, and not all patients have access to these services. Addressing disparities in access to precision medicine is crucial for ensuring that all patients benefit from these advancements.
For example, patients in underserved or rural areas may have limited access to specialized healthcare providers and advanced diagnostic technologies. Efforts to expand access to precision medicine must focus on reducing costs, increasing availability of services, and providing education and support to healthcare providers and patients.
Future Directions and Opportunities
Emerging Therapies
The field of precision medicine is continually evolving, with new therapies and technologies emerging regularly. Advances in genomics, AI, and digital health tools hold significant promise for the future of precision medicine in gastroenterology. These innovations have the potential to enhance diagnosis, improve treatment outcomes, and reduce healthcare costs.
For example, ongoing research into the genetic and molecular basis of GI disorders is uncovering new therapeutic targets and biomarkers. These discoveries are driving the development of novel therapies that can more effectively target the underlying causes of these conditions.
Collaborative Research
Collaboration between research institutions, biotech companies, and healthcare providers is essential for advancing precision medicine. Collaborative research efforts can facilitate the sharing of data, resources, and expertise, accelerating the development of new therapies and improving patient care.
For instance, partnerships between academic institutions and biotech companies can drive innovation in genetic testing and biomarker analysis. Additionally, collaboration between healthcare providers and technology companies can support the integration of digital health tools into clinical practice, enhancing disease management and patient outcomes.
Policy Support
Supportive policies are crucial for promoting research and access to precision medicine for GI disorders. Policymakers can play a significant role in funding research, regulating the use of genetic testing, and ensuring equitable access to advanced diagnostic and treatment options.
For example, government funding for precision medicine research can accelerate the development of new therapies and technologies. Additionally, policies that promote data sharing and collaboration can facilitate the integration of precision medicine into clinical practice, improving patient care and outcomes.
Conclusion
Precision medicine is revolutionizing the diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal disorders. By leveraging genetic and molecular data, healthcare providers can develop personalized treatment plans that improve outcomes, reduce side effects, and enable early intervention. Despite technical, ethical, and accessibility challenges, the future of precision medicine in gastroenterology is promising. Continued research, collaboration, and policy support are essential for advancing this field and ensuring that all patients benefit from these advancements. Stakeholders must support and invest in precision medicine research and treatments for gastrointestinal disorders, paving the way for a future of personalized healthcare.